Note
Click here to download the full example code
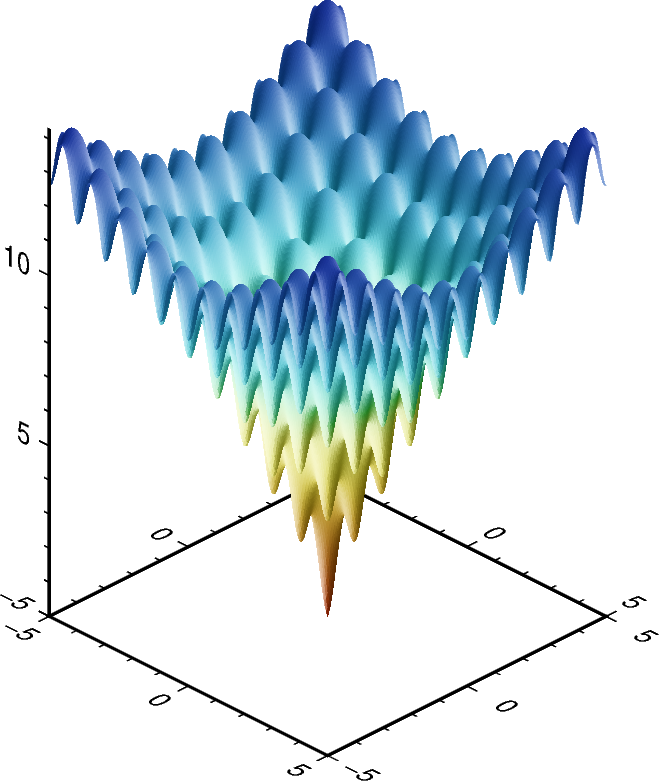
Plotting a surface¶
The pygmt.Figure.grdview method can plot 3-D surfaces with surftype="s". Here,
we supply the data as an xarray.DataArray with the coordinate vectors x and
y defined. Note that the perspective parameter here controls the azimuth and
elevation angle of the view. Specifying the same scale for the projection and zcale
parameters ensures equal axis scaling. We provide a list of two arguments to frame - the
first argument specifies the \(x\)- and \(y\)-axes frame attributes and the
second argument, prepended with "z", specifies the \(z\)-axis frame attributes.
The shading parameter specifies illumination; here we choose an azimuth of
45° with shading="+a45".
Out:
<IPython.core.display.Image object>
import numpy as np
import pygmt
import xarray as xr
# Define an interesting function of two variables, see:
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ackley_function
def ackley(x, y):
return (
-20 * np.exp(-0.2 * np.sqrt(0.5 * (x ** 2 + y ** 2)))
- np.exp(0.5 * (np.cos(2 * np.pi * x) + np.cos(2 * np.pi * y)))
+ np.exp(1)
+ 20
)
# Create gridded data
INC = 0.05
x = np.arange(-5, 5 + INC, INC)
y = np.arange(-5, 5 + INC, INC)
data = xr.DataArray(ackley(*np.meshgrid(x, y)), coords=(x, y))
fig = pygmt.Figure()
# Plot grid as a 3-D surface
SCALE = 0.5 # in centimeter
fig.grdview(
data,
surftype="s",
projection=f"x{SCALE}c",
zscale=f"{SCALE}c",
perspective=[135, 30], # Azimuth southeast (135°), at elevation 30°
frame=["a5f1", "za5f1"],
shading="+a45",
cmap="roma",
)
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 5.938 seconds)